Epigenetics
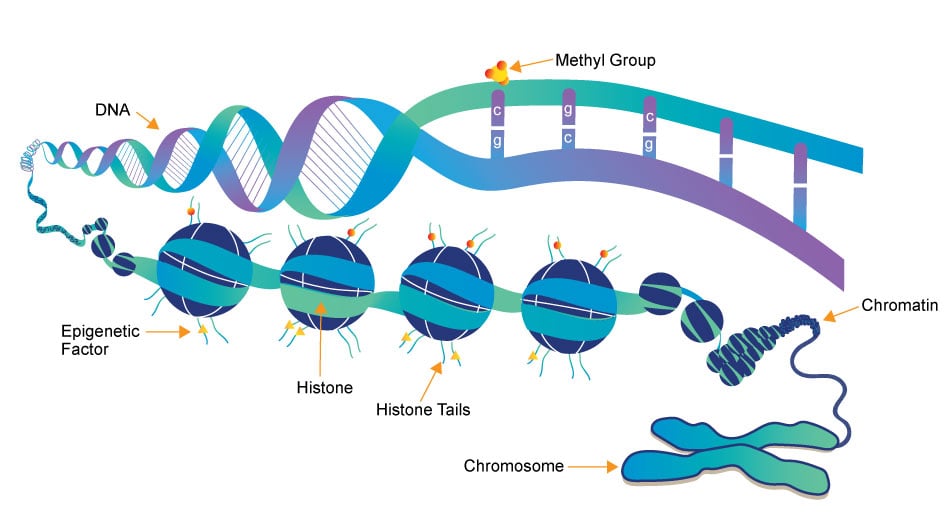

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
Pdia3/ERp57 activator, STAT3 inhibitor
Diosgenin is a steroid sapogenin and the precursor for the semisynthesis of progesterone which in turn was used in early combined oral contraceptive pills.It is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of Dioscorea wild yam, such as the Kokoro.- Rashmi Rawat, .et al. , Food Chemistry Advances, 2022, 1: 100092
-
SIRT1 Activator
SRT1720 is an inhibitor developed intended as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1.- Eleni Pitsillou, .et al. , Comput Biol Chem, 2020, 89: 107408 PMID: 33137690
- Jie Ren, .et al. , Sleep Breath, 2018, Nov 8 PMID: 30411173
- Rowlands BD, .et al. , J Neurochem, 2017, Mar;140(6):903-918 PMID: 27925207
- Adam Khader, .et al. , J Surg Res, 2017, Nov;219:288-295 PMID: 29078895
- Adam Khader, .et al. , Crit Care Med, 2016, Aug; 44(8): e651-e663 PMID: 26963320
- Benjamin D. Rowlands, .et al. , J Neurosci Res., 2015, Jul;93(7):1147-56 PMID: 25677687
- Khader A, .et al. , Transplantation, 2014, 98(2):148-56 PMID: 24918615
-
p53 activator
Tenovin-6 is a analog of tenovin-1. Tenovin-6 inhibits the protein deacetylase activities of purified human SIRT1, SIRT2, and SIRT3 in vitro with IC50 values of 21, 10, and 67 uM, respectively.- Igase M,, .et al. , Exp Cell Res, 2019, Dec 28:111810 PMID: 31891684
-
Pdia3/ERp57 activator, STAT3 inhibitor
Diosgenin glucoside, a saponin compound extracted from Tritulus terrestris L., provides neuroprotection by regulating microglial M1 polarization. Diosgenin glucoside protects against spinal cord injury by regulating autophagy and alleviating apoptosis . -
SIRT1 activator
SRT2104 (GSK2245840) is a selective SIRT1 activator involved in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Phase 2.- Eleni Pitsillou, .et al. , Comput Biol Chem, 2020, 89: 107408 PMID: 33137690
- Liu X, .et al. , Life Sci, 2019, Nov 9:117041 PMID: 31715188
-
SIRT1 Activator
SRT 1720 is a selective activator of human SIRT1 (EC1.5 = 0.16 μM) versus the closest sirtuin homologues, SIRT2 and SIRT3 (SIRT2: EC1.5 = 37 uM; SIRT3: EC1.5 > 300 uM).- A Khader ,etc. Sirtuin 1 activation stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and attenuates renal injury after ischemia-reperfusion. Transplantation, 2014, 98(2), 148-156.
- BD Rowlands ,etc. SIRT1 modulator resveratrol increases brain lactate production and inhibits mitochondrial metabolism while SRT1720 increases oxidative metabolism. , 2015, 93:1147-1156.
- BD Rowlands ,etc. Silent information regulator 1 modulator resveratrol increases brain lactate production and inhibits mitochondrial metabolism, whereas SRT1720 increases oxidative metabolism. Journal of neuroscience research, 2015, 93(7), 1147-1156.
- A Khader ,etc. Sirtuin 1 Stimulation Attenuates Ischemic Liver Injury and Enhances Mitochondrial Recovery and Autophagy. Critical care medicine, 2016, 44(8), e651-e663.
- BD Rowlands ,etc. Acetate metabolism does not reflect astrocytic activity, contributes directly to GABA synthesis, and is increased by silent information regulator 1 activation. Journal of Neurochemistry, 2016, 140(6):903-918. .
-
histone acetyltransferase activator
YF-2 is a highly selective, blood-brain-barrier permeable histone acetyltransferase activator, acetylates H3 in the hippocampus, with EC50s of 2.75 μM, 29.04 μM and 49.31 μM for CBP, PCAF, and GCN5, respectively, shows no effect on HDAC. Anti-cancer and anti-Alzheimer's disease. -
SIRT1 activator
SRT 1720 Hydrochloride is a selective activator of SIRT1 with an EC50 of 0.10 μM, and shows less potent activities on SIRT2 and SIRT3. -
CARM1 inhibitor
SGC2085 hydrochloride is a potent and selective inhibitor of coactivator associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1) with IC50 of 50 nM. -
Pdia3/ERp57 activator, STAT3 inhibitor
Diosgenin palmitate, also known as Diosgenin hexadecanoate, is the hexadecanoic ester of Diosgenin. Diosgenin, a phytosteroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of Dioscorea wild yam, such as the Kokoro.