Epigenetics
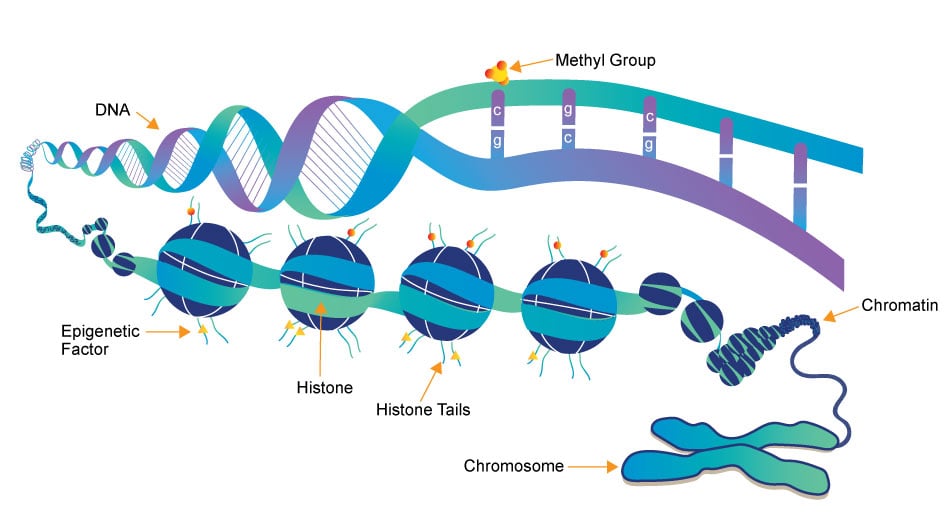

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
HDAC inhibitor
Sodium butyrate (NaB, Butanoic acid sodium salt), sodium salt of butyric acid, is a histone deacetylase inhibitor and competitively binds to the zinc sites of class I and II histone deacetylases (HDACs). -
HDAC inhibitor
Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium Valproate) is an HDAC inhibitor, with IC50 in the range of 0.5 and 2 mM, also inhibits HDAC1 (IC50, 400 μM), and induces proteasomal degradation of HDAC2. -
SIRT1 Activator
SRT1720 is an inhibitor developed intended as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1.- Eleni Pitsillou, .et al. , Comput Biol Chem, 2020, 89: 107408 PMID: 33137690
- Jie Ren, .et al. , Sleep Breath, 2018, Nov 8 PMID: 30411173
- Rowlands BD, .et al. , J Neurochem, 2017, Mar;140(6):903-918 PMID: 27925207
- Adam Khader, .et al. , J Surg Res, 2017, Nov;219:288-295 PMID: 29078895
- Adam Khader, .et al. , Crit Care Med, 2016, Aug; 44(8): e651-e663 PMID: 26963320
- Benjamin D. Rowlands, .et al. , J Neurosci Res., 2015, Jul;93(7):1147-56 PMID: 25677687
- Khader A, .et al. , Transplantation, 2014, 98(2):148-56 PMID: 24918615
-
HDAC Inhibitor
Trichostatin A (TSA) inhibits the HDACs 1, 3, 4, 6 and 10 with IC50 values around 20 nM.- Goudreault M, .et al. , Research Square, 2021, 22 Nov
- Hiroyuki Imuta, .et al. , Heart Vessels, 2020, Jul 16 PMID: 32676696
- Méndez-Blanco C, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2019, Dec 9;11(12). pii: E1984 PMID: 31835431
-
HDAC inhibitor
Vorinostat is an inhibitor of HDACs, inhibiting deacetylation and leading to an accumulation of both hyperacetylated histones and transcription factors.- Amy E Neely, .et al. , Commun Biol, 2023, Jun 23;6(1):664 PMID: 37353594
- Ting-Yu Chang, .et al. , Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, Jun;138:111485 PMID: 33740521
- David Diaz-Carballo, .et al. , Commun Biol, 2021, Mar 3;4(1):276 PMID: 33658617
- Arshdeep Singh, .et al. , Eur J Med Chem, 2021, Apr 5;215:113169 PMID: 33588178
- Shariful Islam, .et al. , Blood Adv, 2020, 4(20): 5297-5310 PMID: 33108458
- Giovanni Bocci, .et al. , ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2020, Oct 14
-
Aurora Kinase inhibitor
VX-680 is a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the Aurora kinases.- Sakamoto K, .et al. , Leukemia, 2018, May 23 PMID: 29795241
- W. Joost Lesterhuis, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 12298 PMID: 26193793
-
PARP inhibitor
MK-4827 is a novel potent, orally bioavailable PARP-1 and PARP-2 inhibitor.- Joseph M Gozgit, .et al. , Cancer cell, 2021, Jul 22;S1535-6108(21)00340-8 PMID: 34375612
- Ann-Katrin Hopp, .et al. , Molecular cell, 2021, Jan 21; 81(2): 340–354 PMID: 33450210
- Bian C, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2019, Feb 11;10(1):693 PMID: 30741937
- Tahira Baloch, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2019, Jan 10;19(1):44 PMID: 30630446
- Khalid Hilmi, .et al. , Sci Adv, 2017, May; 3(5): e1601898 PMID: 28560323
-
HDAC inhibitor
AR-42 is a novel HDAC inhibitor, exhibits biologic activity against malignant mast cell lines via down-regulation of constitutively activated Kit.- Yong-Hui Liao, .et al. , Mol Med Rep, 2018, Feb; 17(2): 2803-2810 PMID: 29257262
-
JAK1/2 Inhibitor
INCB018424 is a potent and selective inhibitor of Janus-associated kinase (JAK) 1 and 2, with IC50 to be 2.7, 4.5 and 332 nM for JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 respectively;- Aya Hasan Alshammari, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, Mar;197:114914 PMID: 35041812
- Daniel Doheny, .et al. , Oncogene, 2020, Oct;39(42):6589-6605 PMID: 32929154
- Rasmus Siersbek, .et al. , Cancer cell, 2020, Jul 6;S1535-6108(20)30311-1 PMID: 32679107
- Brittany M. Duggan, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 1578 PMID: 28484277
- Fujita KI, .et al. , J Pharm Sci, 2017, Sep;106(9):2632-2641 PMID: 28479358
- Kagoya Y, .et al. , Blood., 2014, Nov 6;124(19):2996-3006 PMID: 25217696
-
HDAC6 inhibitor
Tubastatin A is a potent and selective HDAC6 inhibitor with IC50 of 15 nM in a cell-free assay. It is selective against all the other isozymes (1000-fold) except HDAC8 (57-fold).- Isin Cakir, .et al. , Nat Metab, 2022, Jan;4(1):44-59 PMID: 35039672
- Isin Cakir, .et al. , Elife, 2022, Mar 24 PMID: 35323110
-
JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor
TG-101348 is an orally bioavailable, ATP-competitive and selective inhibitor of Janus-associated kinase 2 with potential antineoplastic activity. -
PI3K/HDAC inhibitor
CUDC-907 (Fimepinostat) is a single small molecule inhibitor that targets both PI3K and HDAC. CUDC-907 is more efficacious than either a single PI3K or HDAC inhibitor reference compound or a combination of the two single agents at maximally tolerated doses.- Caner Gunaydın, .et al. , Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2022, Jun;44(3):447-455 PMID: 35291899
- Chie Ishikawa, .et al. , Eur J Haematol, 2020, Eur J Haematol PMID: 32780889
-
Aurora Kinase B/C inhibitor
GSK1070916 is a potent Aurora B/C kinase inhibitor (with IC50 of 3.5 nM/6.5 nM) with broad antitumor activity in tissue culture cells and human tumor xenograft models.
-
Aurora A/B Kinase inhibitor
PF-03814735 is a novel, potent and reversible inhibitor of Aurora A/B with IC50of 0.8 nM/5 nM, is less potent to Flt3, FAK, TrkA, and minimally active to Met and FGFR1. Phase 1. -
JAK inhibitor
NVP-BSK805 is a potent and selective inhibition of polycythemia by the quinoxaline JAK2 inhibitor that potently suppressed recombinant human erythropoietin-induced polycythemia and extramedullary erythropoiesis in mice and rats.
-
JAK inhibitor
BMS-911543 is an orally available small molecule targeting a subset of Janus-associated kinase (JAK) with potential antineoplastic activity. -
PARP inhibitor
BMN-673 is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the nuclear enzyme poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) with potential antineoplastic activity.- Subhajit Chatterjee, .et al. , J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2022, Dec;148(12):3521-3535 PMID: 35962813
- Charles-André Philip, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2017, 17: 638 PMID: 28886696
-
multi-kinase inhibitor
Cenisertib (AS-703569) is a multi-kinase inhibitor that blocks the activity of Aurora-kinase-A/B, ABL1, AKT, STAT5 and FLT3. -
multi-kinase inhibitor
Lestaurtinib (CEP-701;KT-5555) is a multi-kinase inhibitor with potent activity against the Trk family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Lestaurtinib inhibits JAK2, FLT3 and TrkA with IC50s of 0.9, 3 and less than 25 nM, respectively. -
JAK Inhibitor
Baricitinib, also known as INCB028050 or LY3009104, is a selective orally bioavailable JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor with nanomolar potency against JAK1 (5.9 nM) and JAK2 (5.7 nM).- Dandan Wang, .et al. , Adv Rheumatol, 2023, May 16;63(1):22 PMID: 37194022
- Yuki Sasaki, .et al. , JCI Insight, 2022, Apr 8;7(7) PMID: 35393946
- Yutian Lei, .et al. , Kidney Int, 2021, Feb 16 PMID: 33607177
-
Aurora A Kinase inhibitor
MK-5108, also known as VX-689, is a competitive inhibitor of the ATP-binding site of aurora A kinase.- Wei TW, .et al. , Cancer Res, 2017, Jan 15;77(2):494-508 PMID: 28069801
-
MGMT inhibitor
O6BTG-octylglucoside is a potent O6-methylguanine-DNAmethyl-transferase (MGMT) inhibitor, with IC50s of 32 nM in vitro (cell extracts) and 10 nM in HeLa S3 cells. -
BET inhibitor
GSK-525762A is a small molecule inhibitor of the BET (Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal) family -
JAK1/2 inhibitor
Ruxolitinib sulfate (INCB018424 sulfate) is the first potent, selective JAK1/2 inhibitor to enter the clinic with IC50s of 3.3 nM/2.8 nM, and has > 130-fold selectivity for JAK1/2 versus JAK3. -
LKB1/AAK1 dual inhibitor
Pim1/AKK1-IN-1 is a potent multi-kinase inhibitor with Kd values of 35 nM/53 nM/75 nM/380 nM for Pim1/AKK1/MST2/LKB1 respectively, and also inhibits MPSK1 and TNIK. -
JAK inhibitor
Ruxolitinib Phosphate is the phosphate salt form of ruxolitinib, an orally bioavailable Janus-associated kinase (JAK) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic and immunomodulating activities. -
EZH2 inhibitor
GSK126 is a potent, highly selective, S-adenosyl-methionine-competitive, small-molecule inhibitor of EZH2 methyltransferase activity, decreases global H3K27me3 levels and reactivates silenced PRC2 target genes.- Lucy E. Dawson, .et al. , Sarcoma, 2020, 2020: 8647981 PMID: 32300280
- Hirosumi Tamura, .et al. , Oncol Rep, 2018, Aug; 40(2): 635-646 PMID: 29917168
- Dupret B, .et al. , Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2017, Oct;1860(10):1079-1093 PMID: 28887218
- Theresa Baker, .et al. , Oncotarget, 2015, Oct 20; 6(32): 32646-32655 PMID: 26360609
-
BET Bromodomain Inhibitor
GSK1210151A is a novel selective inhibitor of the bromodomain and extra terminal (BET) family proteins BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.- Momeny M, .et al. , Anticancer Drugs, 2018, Nov;29(10):1011-1020 PMID: 30096128
-
JAK Inhibitor
WP1066 is a novel JAK2 inhibitor and it suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in eythroid human cells carrying the JAK2 V617F mutation.- Simona Moravcova, .et al. , Life (Basel), 2021, Oct 18;11(10):1105 PMID: 34685476
-
HDAC inhibitor
Romidepsin strongly inhibits HDAC1 and HDAC2 with IC5N/A of 1.6 nM and 3.9 nM, respectively, but is relatively weak in inhibiting HDAC4 and HDAC6 with IC5N/A 25 nM and 79N/A nM, respectively.- Yu-Fang Liu, .et al. , J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2022, Jun;36(6):e23044 PMID: 35499365
- David Diaz-Carballo, .et al. , Commun Biol, 2021, Mar 3;4(1):276 PMID: 33658617
- Eva Hesping, .et al. , Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist, 2020, 14: 249-256
- Shariful Islam, .et al. , Blood Adv, 2020, 4(20): 5297-5310 PMID: 33108458
- Elena Netchiporouk, .et al. , Oncotarget, 2017, Nov 10; 8(56): 95981-95998 PMID: 29221181
- Ivan V. Litvinov, .et al. , Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(14): 3799-3808 PMID: 24850846
- Ivan V Litvinov, .et al. , Cell Cycle., 2014, 15; 13(18): 2975-2982 PMID: 25486484
-
HDAC6 inhibitor
ACY-1215 selectively targets and binds to HDAC6, thereby disrupting the Hsp90 protein chaperone system through hyperacetylation of Hsp90 and preventing the subsequent aggresomal protein degradation. -
Pim Inhibitor
SIM-4a is a Pim kinase inhibitor that blocks mTORC1 activity via activation of AMPK. Mostly potent to Pim-2, does not significantly inhibit any other serine/threonine- or tyrosine-kinases.- Liong S, .et al. , Placenta, 2017, May;53:101-112 PMID: 28487013
-
FLT3 inhibitor
TG-02 is a novel small molecule potent CDK/JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor. -
HDAC Inhibitor
CI-994 is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor and induces histone hyperacetylation in living cells. -
Pim inhibitor
TCS PIM-1 4a is a selective and ATP-competitive Pim kinase inhibitor (IC50 values = 24 and 100 nM for Pim-1 and Pim-2, respectively).