Epigenetics
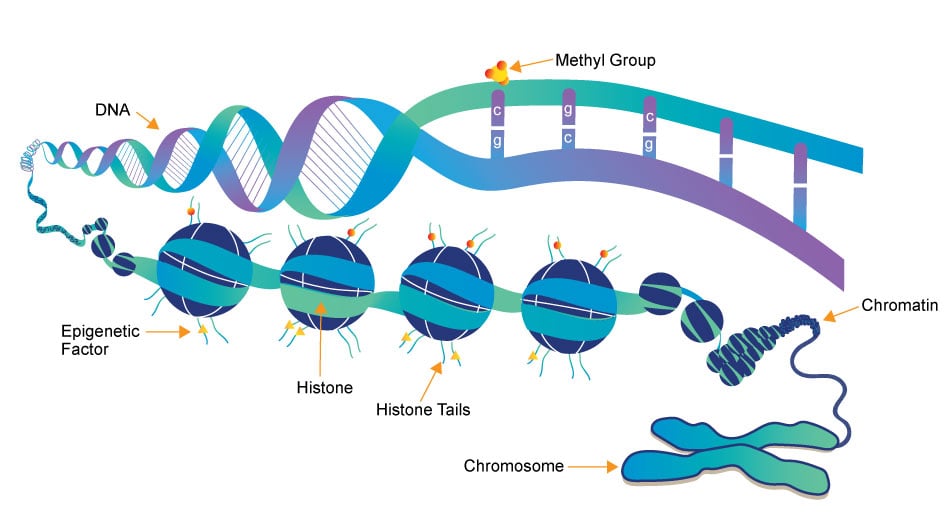

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
Dynamin inhibitor
Dynamin Inhibitory Peptide is a peptide inhibitor of the GTPase dynamin. -
PKA inhibitor
PKA inhibitor fragment (6-22) amide is a synthetic peptide that acts as a protein kinase inhibitor. -
PKC inhibitor
PKC (19-36), pseudosubstrate peptide inhibitor of protein kinase C (IC50 = 0.18 uM). -
Ca 2+ /Mg 2+ -ATPase inhibitor
Glucagon (19-29) (human) is a potent Ca 2+ /Mg 2+ -ATPase inhibitor. -
Bax inhibitor
Bax inhibitor peptide P5, cell-permeable synthetic peptide inhibitor of Bax translocation to mitochondria; designed from Ku70, a protein that is suggested to suppress the mitochondrial translocation of Bax. Inhibits Bax-mediated apoptosis in vitro. -
Bax inhibitor
Bax inhibitor peptide V5, cell-permeable synthetic peptide inhibitor of Bax translocation to mitochondria; designed from Ku70, a protein that is suggested to suppress the mitochondrial translocation of Bax. Inhibits Bax-mediated apoptosis in vitro. -
Bax inhibitor
Bax inhibitor peptide, negative control, negative control peptide for the Bax inhibitor peptides V5 and P5 , which inhibit Bax translocation to mitochondria and Bax-mediated apoptosis in vitro. -
Fibronectin Inhibitor
RGDS peptide inhibits thrombin-induced binding of platelets to fibronectin, fibrinogen α, and von Willebrand factor with IC50 value of 10 μM. -
MUC1-C oncoprotein inhibitor
GO-203 TFA is a potent MUC1-C oncoprotein inhibitor. GO-203 TFA is an anti-cancer peptide for targeting intracellular proteins. -
Complement factor C3 inhibitor
POT-4 (AL-78898A), a Compstatin derivative, is a potent inhibitor of complement factor C3 activation. POT-4 can be used for age-related macular degeneration research -
FGFR3 inhibitor
VSPPLTLGQLLS is a small peptide FGFR3 inhibitor, peptide P3, inhibits FGFR3 phosphorylation. VSPPLTLGQLLS inhibits 9-cisRA-induced tracheal lymphangiogenesis and blocks lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) proliferation, migration, and tubule formation. -
CKLF1/CCL17 inhibitor
CKLF1-C19 is the C-terminal peptide of human chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1). CKLF1-C19 interacts with CCR4, and inhibits chemotaxis induced by both CKLF1 and CCL17. CKLF1-C19 can suppress allergic lung inflammation via inhibiting chemotaxis mediated by CCR3 and CCR4. -
ACE inhibitor
Bradykinin potentiator B (Bradykinin potentiating peptide B) is venom of Agkistrodon halys blomhoffi. Bradykinin potentiator B is a potent ACE inhibitor. Bradykinin potentiator inhibits the activity of bradykinin inhibitory peptidase. -
anti-HIV-1 fusion inhibitor
Enfuvirtide (T20; DP178) acetate is an anti-HIV-1 fusion inhibitor peptide.