Epigenetics
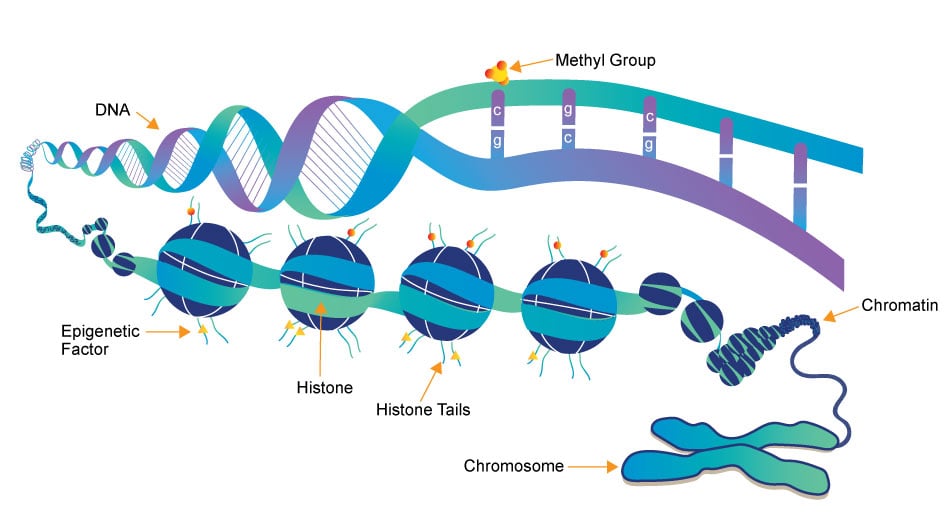

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
- Amyloid b-Peptide (1-40) (human) is a peptide processed from the amyloid precursor protein (APP).
- Amyloid b-Peptide (1-43) (human), amyloid β peptide fragment. Highly toxic, showing higher neurotoxicity compared to Aβ40 and Aβ42.
- Beta-amyloid (1-11) (Abeta) is a peptide with the sequence H-{Asp}{Ala}{Glu}{Phe}{Arg}{His}{Asp}{Ser}{Gly}{Tyr}{Glu}-OH,which is processed from the Amyloid precursor protein.
- Beta-amyloid protein (A beta), a 39-43 amino acid peptide composed of a portion of the transmembrane domain and the extracellular domain of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), is also the principal component of amyloid.
-
T cell activator
beta-Interleukin I (163-171), human, a peptide. Interleukins are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins/signaling molecules) that were first seen to be expressed by white blood cells (leukocytes). -
GnRH agonist
Goserelin is a synthetic decapeptide analog of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) with antineoplastic activity. - Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is an endogenous neuropeptide hormone that is involved in stress responses, depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
-
Endogenous galanin receptor agonist
Galanin (1-30) (human) is an endogenous peptide with multiple endocrine, metabolic and behavioral effects -
Neuropeptide Hormone
Secretin is a neuropeptide hormone that regulates secretion from the stomach, pancreas, and liver. -
Amylin receptor ligand
Amylin (rat) is a potent and high affinity ligand of Amylin receptor AMY1 and AMY3 receptors and variably of AMY2 receptors; binding studies are generally used for the latter receptor.
- Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (7-36) Amide is a potent glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide produced by post-translational processing of proglucagon in intestinal L-cells.
- Ying Zhou, .et al. , Adv Biol (Weinh), 2022, Nov 14 PMID: 36373695
-
α3β4 nAChR ligand
AT-1001 is a tight junction regulator and reverses leaky junctions to their normally closed state. It is being studied in people with celiac disease -
CGRP receptor antagonist
HCGRP-(8-37) is a human calcitonin gene-related peptide (hCGRP) fragment and also an antagonist of CGRP receptor.
-
neuroprotectant
Trofinetide, also known as NNZ-2566, is a glypromate (or Gly-Pro-Glu) analog and neuroprotectant. NNZ-2566, a glypromate analog, improves functional recovery and attenuates apoptosis and inflammation in a rat model of penetrating ballistic-type brain injury. - Neuronostatin-13 human is a 13-amino acid peptide hormone encoded by the somatostatin gene and plays an important role in the regulation of hormonal and cardiac function.
-
Fibronectin Inhibitor
RGDS peptide inhibits thrombin-induced binding of platelets to fibronectin, fibrinogen α, and von Willebrand factor with IC50 value of 10 μM. - Bentiromide is a peptide used as a screening test for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and to monitor the adequacy of supplemental pancreatic therapy. It is given by mouth as a noninvasive test. The amount of 4-aminobenzoic acid and its metabolites excreted in the urine is taken as a measure of the chymotrypsin-secreting activity of the pancreas.
- Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It works to raise the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. Its effect is opposite that of insulin, which lowers the glucose.
- Angiotensin II human is a vasoconstrictor that acts on the AT1 and the AT2 receptor.
-
gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist
Buserelin Acetate is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH agonist). - Octreotide is a somatostatin analog that binds to the somatostatin receptor, mainly subtypes 2, 3, and 5, increases Gi activity, and reduces intracellular cAMP production.
- CEP dipeptide 1 is a CEP dipeptide with potent angiogenic activity; mediators of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
-
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist
Exendin-4 Acetate (Exenatide acetate), a 39 amino acid peptide, is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist with an IC50 of 3.22 nM. -
N-cadherin antagonist
ADH-1 trifluoroacetate is an N-cadherin antagonist, which inhibits N-cadherin mediated cell adhesion. -
regenerative peptide
Rusalatide acetate (TP508 amide acetate), a regenerative peptide, mitigates radiation-induced gastrointestinal damage by activating stem cells and preserving crypt integrity. - D-γ-Glutamyl-D-glutamic acid is a poly(γ-glutamic acid) of clusters of D- and D-glutamic acid repeating units in a linear chain.
-
GnRH peptide agonist
Triptorelin is a synthetic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) peptide agonist that binds to the GnRH receptor. It inhibits the growth of DU145, LNCaP, and PC3 prostate and OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cells. - Tirzepatide (LY3298176, GIP/GLP-1 RA, TZP) is a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist. Tirzepatide differentially induces internalization of the GIP and GLP-1 receptors with EC50 values of 18.2 nM and 18.1 nM, respectively.
-
oxytocin receptor ligand
Oxytocin (α-Hypophamine) acetate is a pleiotropic, hypothalamic peptide known for facilitating parturition, lactation, and prosocial behaviors. Oxytocin acetate can function as a stress-coping molecule with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and protective effects especially in the face of adversity or trauma. - Cyclic somatostatin (SRIF-14) is a growth hormone-release inhibiting factor used in the research of severe, acute hemorrhages of gastroduodenal ulcers. Cyclic somatostatin is a neuropeptide co-stored with acetylcholine in the cardiac parasympathetic innervation, exerts influences directly on contraction of ventricular cardiomyocytes. Cyclic somatostatin inhibits the contractile response of isoprenaline with an IC50 value of 13 nM. Cyclic somatostatin can be used for the research of cardiovascular disease.
- Argipressin (Arg8-vasopressin) binds to the V1, V2, V3-vascular arginine vasopressin receptor, with a Kd value of 1.31 nM in A7r5 rat aortic smooth muscle cells for V1.
- L-Carnosine is a dipeptide of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine and has the potential to suppress many of the biochemical changes that accompany aging.