Epigenetics
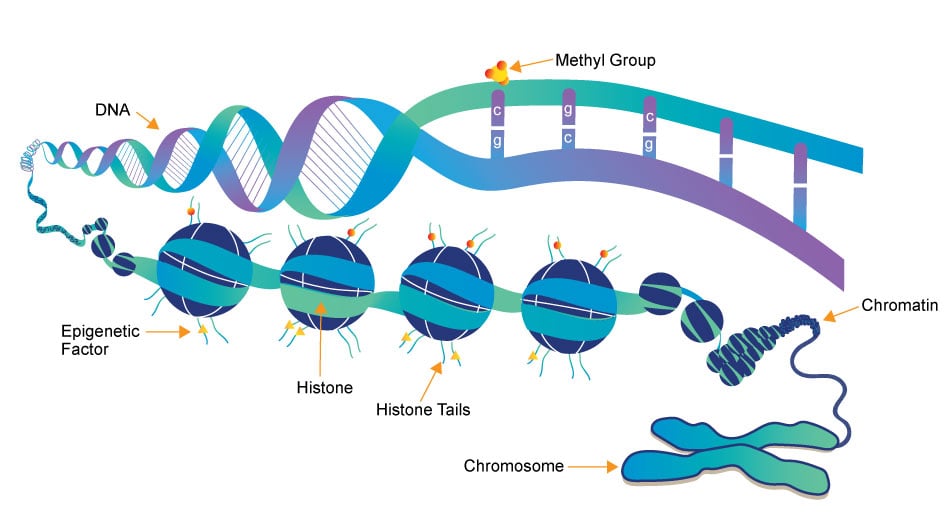

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
- Cibinetide (ARA290) is an EPO-derivative, acting as a specific agonist of erythropoietin/CD131 heteroreceptor, and used for neurological disease treatment.
- Tertiapin-Q is a highly selective blocker of GIRK1/4 heterodimer and ROMK1 (Kir1.1).
- Difelikefalin (CR-845; FE-202845) is a peripherally restricted and selective agonist of kappa opioid receptor (KOR). Difelikefalin produces anti-inflammatory effects and has the potential in modulating pruritus in conditions such as chronic kidney disease.
- Argireline (Acetyl hexapeptide-3) is a non-toxic, skin-permeable, antiwrinkle peptide. Argireline significantly inhibits Ca2+ dependent neurotransmitter release (acetylcholine) at the neuromuscular junction. Argireline has antiwrinkle and anti-aging activity.
- Epsilon-V1-2 (ε-V1-2), a PKCε-derived peptide, is a selective PKCε inhibitor. Epsilon-V1-2 inhibits the translocationof PKCε, but not α-, β-, and δPKC.
-
GLP-1 receptor agonist
Oxyntomodulin (bovine, porcine), a 37-amino acid peptide hormone, is a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. - Nociceptin, a heptadecapeptide, is the endogenous ligand of the nociceptin receptor, acting as a potent anti-analgesic.
- Teduglutide is a dipeptidyl peptidase IV resistant glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) analogue. Teduglutide is associated with trophic effects on gut mucosa. Teduglutide can be used for the research of short bowel syndrome (SBS) and Crohn's disease (CD).
- Gastrin-Releasing Peptide, human (GRP) belongs to the bombesin-like peptide family, and is not a classical hypothalamic-hypophyseal regulatory hormone since it plays only a perfunctory role in the mediation of pituitary hormone release.
- Pramlintide acetate is a polypeptide analogue of human amylin. Pramlintide acetate, an antidiabetic agent, is antineoplastic in colorectal cancer.
- C-Type Natriuretic Peptide (CNP) (1-22), human (TFA),a 1-22 fragment of CNP, is a natriuretic peptide receptor B (NPR-B) agonist. C-Type Natriuretic Peptide (CNP) (1-22), human (TFA) inhibits cAMP synthesis stimulated by the physiological agonists histamine and 5-HT or directly by Forskolin. CNP is a potent, endothelial-derived relaxant and growthinhibitory factor.
- N-Acetylcarnosine, a natural histidine-containing dipeptide, is a source of pharmacological principal L-carnosine. N-Acetylcarnosine is a potent ophthalmic agent in human cataracts.
- Tat-NR2B9c TFA (Tat-NR2Bct TFA) is a postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) inhibitor, with EC50 values of 6.7 nM and 670 nM for PSD-95d2 (PSD-95 PDZ domain 2) and PSD-95d1, respectively. Tat-NR2B9c TFA disrupts the PSD-95/NMDAR interaction, inhibiting NR2A and NR2B binding to PSD-95 with IC50 values of 0.5 μM and 8 μM, respectively. Tat-NR2B9c TFA also inhibits neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS)/PSD-95 interaction, and possesses neuroprotective efficacy.
-
Beinaglutide is a human GLP-1 polypeptide that shares almost 100% homology with human GLP-1 (7-36). Beinaglutide displays does-dependent effects in glycemic control, inhibiting food intake and gastric empty and promoting weight loss. Beinaglutide has the potential for the research of overweight/obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
- Sulanemadlin (ALRN-6924) is a potent p53-based peptidomimetic macrocycles. Sulanemadlin is a inhibitor of the p53-MDM2, p53-MDMX, or both p53 and MDM2 and MDMX protein-protein interactions. Sulanemadlin can be used for cancers research.
- AMY-101 TFA (Cp40 TFA), a peptidic inhibitor of the central complement component C3 (KD = 0.5 nM), inhibits naturally occurring periodontitis in non-human primates (NHPs). AMY-101 (Cp40) exhibits a favorable anti-inflammatory activity in models with COVID-19 severe pneumonia with systemic hyper inflammation.
- GLP-2(1-33) (human) is an enteroendocrine hormone which can bind to the GLP-2 receptor and stimulate the growth of intestinal epithelium.
- Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) (1-28), rat is a major circulating form of ANP in rats, potently inhibits Angiotensin II (Ang II)-stimulated endothelin-1 secretion in a concentration-dependent manner.
- β-Endorphin, human, a prominent endogenous peptide, existing in the hypophysis cerebri and hypothalamus, is an agonist of opioid receptor, with preferred affinity for μ-opioid receptor and δ-opioid receptor; β-Endorphin, human exhibits antinociception activity.
- PAMP-12(human, porcine) is a major component of immunoreactive (ir)-PAMP, is processed from the adrenomedullin precursor, is a potent hypotensive peptide and participates in cardiovascular control.
- Luteinizing hormone (human), a heterodimeric glycoprotein hormone produced by the pituitary gland (LH), plays key roles in human reproduction.
- Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) free acid is a neuropeptide. Calcitonin gene-related peptide can be used for the research of nociception, ingestive behaviour and modulation of the endocrine systems.
- (S)-2-((((9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)amino)-5-(tert-butoxy)-5-oxopentanoic acid is a glutamic acid derivative.
- c-Myc Peptide (TFA) is a synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal amino acids (410-419) of human c-myc protein, and participates in regulation of growth-related gene transcription.
-
GLP-1 agonist
Lixisenatide acetate is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that can be used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). - (S)-2-Amino-3-(4-bromophenyl)propanoic acid is a phenylalanine derivative.
- γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (L-γ-Glutamyl-(S)-Allyl-Cysteine) is a naturally occurring organosulfur compound found in garlic. γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine has antiglycative effect and shows radical-scavenging and metal-chelating capacities.
-
μ-opioid receptor agonist
Dermorphin is a natural heptapeptide μ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonist found in amphibian skin. Inhibition of neuropathic pain. - TAT-cyclo-CLLFVY is a cyclic peptide inhibitor of HIF-1 heterodimerization that inhibits hypoxia signaling in cancer cells. TAT-cyclo-CLLFVY disrupts HIF-1α/HIF-1β protein-protein interaction with an IC50 of 1.3 μM.
- Cyclo(Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Phe-Cys) (Cyclo RGDfC), a cyclic RGD peptide which has high affinity to αvβ3, can disrupt cell integrin interactions. Cyclo(Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Phe-Cys) inhibits pluripotent marker expression in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and the tumorigenic potential of mESCs in vivo. Cyclo(Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Phe-Cys) can be used in the research of tumors.
-
Complement factor C3 inhibitor
POT-4 (AL-78898A), a Compstatin derivative, is a potent inhibitor of complement factor C3 activation. POT-4 can be used for age-related macular degeneration research - Fmoc-Ala-Glu-Asn-Lys-NH2 is a selective asparagine endopeptidase (AEP) inhibitor peptide and suppresses amyloid precursor protein (APP) cleavage. AEP, a pH-controlled cysteine proteinase, is activated during ageing and mediates APP proteolytic processing.
- Felypressin acetate (PLV-2 acetate) is a non-catecholamine vasoconstrictor and a vasopressin 1 agonist. Felypressin acetate is widely used in dental procedures.
- D-Ala-Lys-AMCA hydrochloride is a known proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter 1 (PEPT1) substrate that emits blue fluorescence. D-Ala-Lys-AMCA hydrochloride may be transported into liver cancer cells and Caco-2 cells based on fluorescence analysis. D-Ala-Lys-AMCA hydrochloride can be used for characterizing PEPT1-specific substrates or inhibitors.
- Cholecystokinin Octapeptide, desulfated is a synthetic desulfated octapeptides of cholecystokinin (CCK).
- Ac-IETD-AFC is a fluorogenic substrate of caspase-8, caspase-3, caspase-10, and granzyme B.
- Phalloidin-TRITC is a fluorescein derivative of Phalloidin, which can specifically label myof lin and display red fluorescence when labeled and can be observed using Tesred channels.