Epigenetics
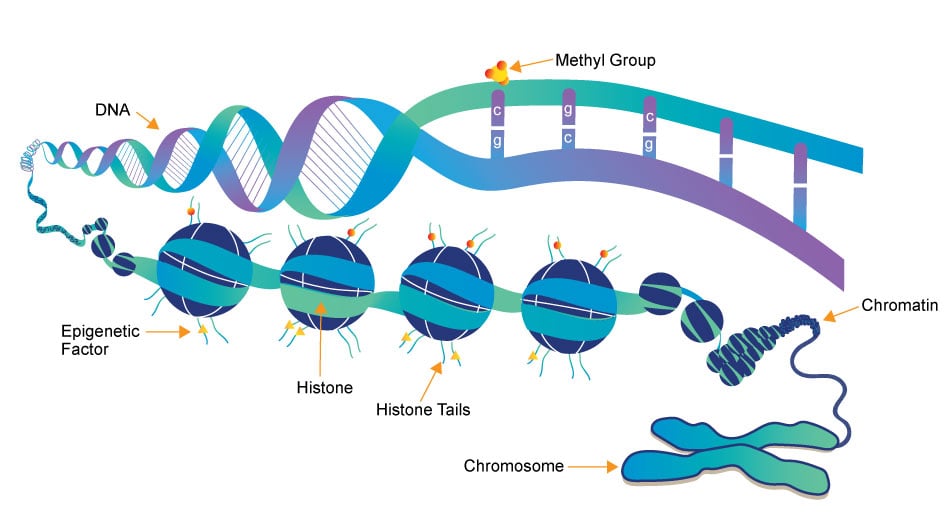

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor
TG-101348 is an orally bioavailable, ATP-competitive and selective inhibitor of Janus-associated kinase 2 with potential antineoplastic activity. -
FLT3 inhibitor
TG-02 is a novel small molecule potent CDK/JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor. -
JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor
Pacritinib, also known as SB1518, is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) and the JAK2 mutant JAK2V617F with potential antineoplastic activity. Pacritinib competes with JAK2 for ATP binding, which may result in inhibition of JAK2 activation, inhibition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and so caspase-dependent apoptosis.- Daniel Doheny, .et al. , Oncogene, 2020, Oct;39(42):6589-6605 PMID: 32929154
-
multi-targeted kinase inhibitor
ENMD-2076 Tartrate is a multi-targeted kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 1.86, 14, 58.2, 15.9, 92.7, 70.8, 56.4 nM for Aurora A, Flt3, KDR/VEGFR2, Flt4/VEGFR3, FGFR1, FGFR2, Src, PDGFRα, respectively. -
FLT3 inhibitor
AC220 (Quizartinib) is a uniquely potent and selective FLT3 inhibitor with IC50 of 0.56±0.3 nM and >10 mM for MC4-11 and A375, respectively.
- Nicholas R Anderson, .et al. , Leukemia, 2023, Mar;37(3):560-570 PMID: 36550214
- N Naganna, .et al. , EBioMedicine, 2019, Jan 24. pii: S2352-3964(19)30012-X PMID: 30686755
- Cong Li, .et al. , Mol Cancer Ther., 2015, Feb;14(2):375-83. PMID: 25487917
- Yaping Zhang, .et al. , J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn., 2014, 41(6): 675-691 PMID: 25326874
-
RTK inhibitor
Dovitinib is a small-molecule multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which inhibits Ba/F3 cells transformed to IL3 independence by ZNF198-FGFR1 or BCR-FGFR1 with IC50 values of 150 nM and 90 nM, respectively. -
Syk Inhibitor
R406 is an orally available spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 41 nM.- Gabriella Leung, .et al. , JCI insight, 2021, Dec 8;6(23):e149376 PMID: 34673575
-
FLT3 Inhibitor
Tandutinib (MLN518) inhibits the autophosphorylation of FLT3, c-KIT and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinases, thereby inhibiting cellular proliferation and inducing apoptosis. -
VEGFR inhibitor
XL184 free base (Cabozantinib) is a small molecule designed to inhibit multiple receptor tyrosine kinases, specifically MET and VEGFR2.- Fujita KI, .et al. , J Pharm Sci, 2017, Sep;106(9):2632-2641 PMID: 28479358
-
PDGFR/FLT3 Inhibitor
Crenolanib (CP-868596) is an orally bioavailable, selective small molecule inhibitor of the PDGFR tyrosine kinase, inhibiting both PDGFRA and PDGFRB at picomolar concentrations.- N Naganna, .et al. , EBioMedicine, 2019, Jan 24. pii: S2352-3964(19)30012-X PMID: 30686755
-
multiple receptor tyrosine kinases inhibitor
Cabozantinib S-malate (XL184 S-malate) is a potent multiple receptor tyrosine kinases inhibitor that inhibits VEGFR2, c-Met, Kit, Axl and Flt3 with IC50s of 0.035, 1.3, 4.6, 7 and 11.3 nM, respectively.- Paula Sagmeister, .et al. , J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, Jul 9;9:595-607 PMID: 35845819
- Aya Hasan Alshammari, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, Mar;197:114914 PMID: 35041812
-
RTK inhibitor
Dovitinib is a small-molecule multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which inhibits Ba/F3 cells transformed to IL3 independence by ZNF198-FGFR1 or BCR-FGFR1 with IC50 values of 150 nM and 90 nM, respectively.- Yunping Hu, .et al. , Cancer Lett, 2022, Oct 28;547:215867 PMID: 35985510
-
FLT3/Axl inhibitor
Gilteritinib is a potent FLT3/AXL inhibitor, which showed potent antileukemic activity against AML with either or both FLT3-ITD and FLT3-D835 mutations.- Mohammad Azhar, .et al. , Blood Adv, 2022, Aug 31 PMID: 36044389
-
CSF1/Kit/FLT3 inhibitor
Pexidartinib is a small-molecule receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor of KIT, CSF1R and FLT3 with potential antineoplastic activity.- Lu Luo, .et al. , J Neuroinflammation, 2022, Jun 11;19(1):141 PMID: 35690810
- Sarah R Anderson,, .et al. , bioRxiv, 2022, 01.05.475126
- Hannah D Mason, .et al. , JCI Insight, 2021, Oct 8;6(19):e149229 PMID: 34428178
- Chritica Lodder, .et al. , Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2021, Jun 8;9(1):108 PMID: 34103079
- Anderson SR, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2019, May 14;27(7):2002-2013.e5 PMID: 31091440
-
FLT3/AXL inhibitor
Gilteritinib hemifumarate is a potent FLT3/AXL inhibitor with IC50 of 0.29 nM/0.73 nM, respectively. -
multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Amuvatinib hydrochloride (MP470 hydrochloride) is an orally bioavailable multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent activity against mutant c-Kit, PDGFRα, Flt3, c-Met and c-Ret. -
IRAK4/FLT3 inhibitor
Emavusertib, also known as CA-4948 is a potent IRAK4/FLT3 inhibitor with anti-tumor activity. CA-4948 demonstrated good cellular activity in ABC DLBCL and AML cell lines. CA-4948 demonstrated moderate to high selectivity in a panel of 329 kinases as well as exhibited desirable ADME and PK profiles including good oral bioavailability in mice, rat, and dog and showed >90% tumor growth inhibition in relevant tumor models with excellent correlation with in vivo PD modulation.