Epigenetics
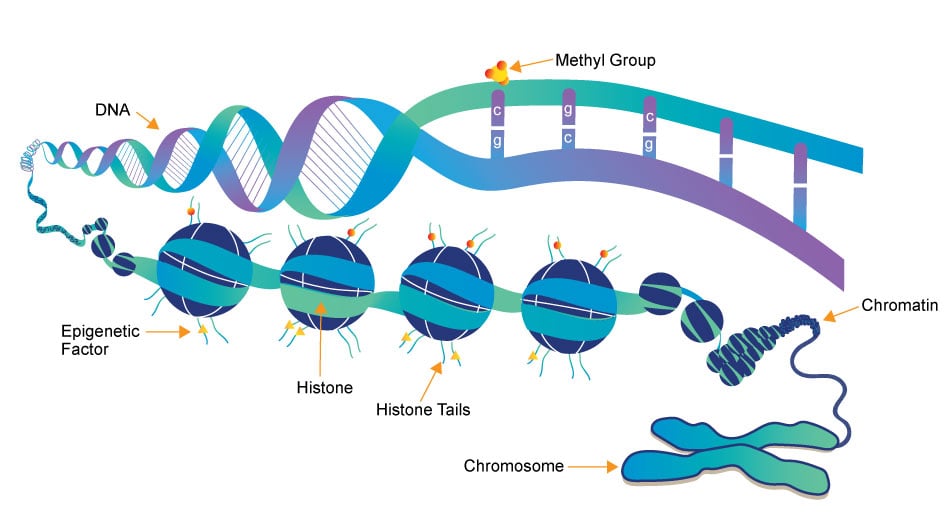

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
LSD1 inhibitor
GSK2879552 is an orally available, irreversible, inhibitor of lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1), with potential antineoplastic activity.- Nicolas A Fraunhoffer, .et al. , EBioMedicine, 2023, Jun;92:104602 PMID: 37148583
-
HDAC/ACE inhibitor
Sinapinic acid (Sinapic acid) is a phenolic compound isolated from Hydnophytum formicarum Jack. Rhizome, acts as an inhibitor of HDAC, with an IC50 of 2.27 mM, and also inhibits ACE-I activity. Sinapinic acid posssess potent anti-tumor activity, induces apoptosis of tumor cells. -
MEK/Aurora Inhibitor
BI-847325 is an orally bioavailable, and selective dual MEK/Aurora kinase inhibitor with IC50 of 3 nM, 25 nM, 15 nM, 25 nM, and 4 nM for Xenopus laevis Aurora B, human Aurora A and Aurora C, as well as human MEK1 and MEK2, respectively. Phase 1.- Hilda Samimi, .et al. , Cancer Cell Int, 2022, Dec 8;22(1):388 PMID: 36482411
- Hilda Samimi, .et al. , Thyroid Res, 2021, Dec 3;14(1):27 PMID: 34861882
- Hilda Samimi, .et al. , DARU J Pharm Sci, 2019, 1-7 PMID: 31077090
-
TNKS2 inhibitor
NVP-TNKS656 is a highly potent, selective, and orally active TNKS2 inhibitor with IC50 of 6 nM; > 300 fold selectivity against PARP1 and PARP2. -
Calcineurin/PP2B inhibitor
Ascomycin is an ethyl analog of tacrolimus (FK506) with strong immunosuppressant properties. It has been researched for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and skin diseases, and to prevent rejection after an organ transplant. -
LSD1 Inhibitor
ORY-1001 is an orally active and selective lysine-specific demethylase LSD1/KDM1A inhibitor with IC50 of <20 nM, with high selectivity against related FAD dependent aminoxidases. Phase 1. -
Selective SIRT2 inhibitor
SirReal2 is a potent and selective Sirt2 inhibitor with IC50 of 140 nM.- Yang Li, .et al. , Neoplasia, 2018, Jul; 20(7): 745-756 PMID: 29925042
-
JAK2 inhibitor
NS-018 hydrochloride is a novel highly selective JAK2 inhibitor. -
JAK2 inhibitor
NS-018 maleate is an ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of JAK2 with IC50 of 470nM in Ba/F3-JAK2V617F cells . have30-50-fold greater selectivity for JAK2 over other JAK-family kinases, such as JAK1, JAK3 and tyrosine kinase 2. -
EZH2 inhibitor
Lirametostat (CPI-1205) is a highly potent (biochemical IC50 = 0.002 μM, cellular EC50 = 0.032 μM) and selective inhibitor of EZH2.
-
BET inhibitor
BET-BAY 002 is a potent BET inhibitor; shows efficacy in a multiple myeloma model. -
KDM inhibitor
2,4-Pyridinedicarboxylic Acid (2,4-PDCA) is an inhibitor of histone lysine-specific demethylases that targets on JMJD2A (KDM4A), KDM4C, KDM4E (IC50, 1.4 μM), KDM5B (IC50, 3 μM), KDM6A and other 2-oxogynases.