Epigenetics
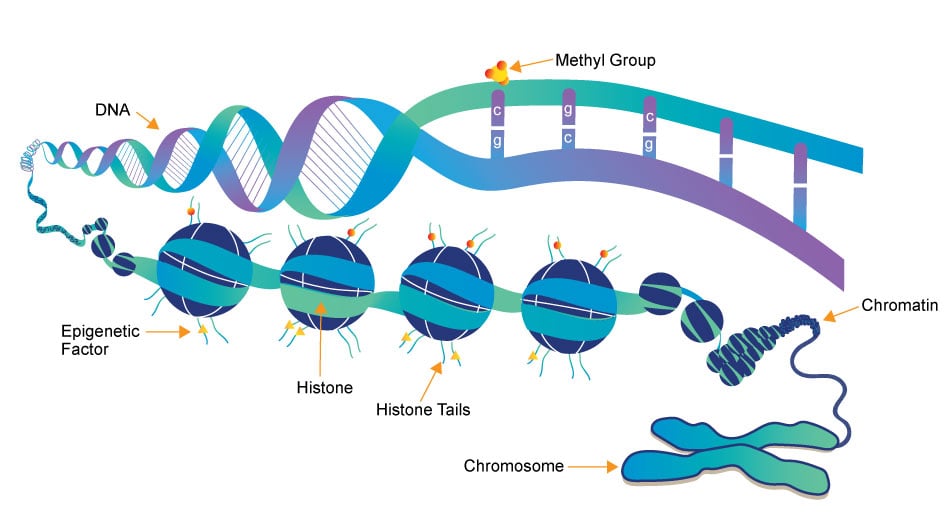

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
PARP inhibitor
AG14361 is a potent PARP inhibitor, enhanced TMZ cytotoxicity in MMR(mismatch repair)-proficient / deficient cells.- Vimal Pandey, .et al. , Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, Article number: 5012 PMID: 30899038
-
HDAC inhibitor
JNJ-26481585 (Quisinostat) is a pan-HDAC inhibitor with marked potency toward HDAC1 (IC(50), 0.16 nmol/L).- Minoru Ueda, .et al. , Plant Physiol, 2017, Dec; 175(4): 1760-1773 PMID: 29018096
-
CDK/Aurora A/B Inhibitor
JNJ-7706621 is pan-CDK inhibitor with the highest potency on CDK1/2 with IC50 of 9 nM/4 nM and showing >6-fold selectivity for CDK1/2 than CDK3/4/6 in cell-free assays. It also potently inhibits Aurora A/B and has no activity on Plk1 and Wee1.- Yuta Tanizaki, .et al. , Commun Biol, 2022, 5: 112 PMID: 35132135
-
HDAC Inhibitor
LAQ824 (NVP-LAQ824) is a potent novel histone deacetylase inhibitor with significant activity against multiple myeloma.- De-Run Chen, .et al. , Appl Mater Today, 2022, 26: 101363
-
Aurora inhibitor
Danusertib (PHA-739358) is an Aurora kinase inhibitor for Aurora A/B/C with IC50 of 13 nM/79 nM/61 nM in cell-free assays, modestly potent to Abl, TrkA, c-RET and FGFR1, and less potent to Lck, VEGFR2/3, c-Kit, CDK2, etc. Phase 2- Vijaya Bharti, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2022, Dec 20;41(12):111826 PMID: 36543138
-
HDAC Inhibitor
Trichostatin A (TSA) inhibits the HDACs 1, 3, 4, 6 and 10 with IC50 values around 20 nM.- Goudreault M, .et al. , Research Square, 2021, 22 Nov
- Hiroyuki Imuta, .et al. , Heart Vessels, 2020, Jul 16 PMID: 32676696
- Méndez-Blanco C, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2019, Dec 9;11(12). pii: E1984 PMID: 31835431
-
JAK inhibitor
NVP-BSK805 is a potent and selective inhibition of polycythemia by the quinoxaline JAK2 inhibitor that potently suppressed recombinant human erythropoietin-induced polycythemia and extramedullary erythropoiesis in mice and rats.
-
JAK inhibitor
BMS-911543 is an orally available small molecule targeting a subset of Janus-associated kinase (JAK) with potential antineoplastic activity. -
Aurora A Kinase inhibitor
MK-5108, also known as VX-689, is a competitive inhibitor of the ATP-binding site of aurora A kinase.- Wei TW, .et al. , Cancer Res, 2017, Jan 15;77(2):494-508 PMID: 28069801
-
MGMT inhibitor
O6BTG-octylglucoside is a potent O6-methylguanine-DNAmethyl-transferase (MGMT) inhibitor, with IC50s of 32 nM in vitro (cell extracts) and 10 nM in HeLa S3 cells. -
HDAC inhibitor
Romidepsin strongly inhibits HDAC1 and HDAC2 with IC5N/A of 1.6 nM and 3.9 nM, respectively, but is relatively weak in inhibiting HDAC4 and HDAC6 with IC5N/A 25 nM and 79N/A nM, respectively.- Yu-Fang Liu, .et al. , J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2022, Jun;36(6):e23044 PMID: 35499365
- David Diaz-Carballo, .et al. , Commun Biol, 2021, Mar 3;4(1):276 PMID: 33658617
- Eva Hesping, .et al. , Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist, 2020, 14: 249-256
- Shariful Islam, .et al. , Blood Adv, 2020, 4(20): 5297-5310 PMID: 33108458
- Elena Netchiporouk, .et al. , Oncotarget, 2017, Nov 10; 8(56): 95981-95998 PMID: 29221181
- Ivan V. Litvinov, .et al. , Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(14): 3799-3808 PMID: 24850846
- Ivan V Litvinov, .et al. , Cell Cycle., 2014, 15; 13(18): 2975-2982 PMID: 25486484
-
HDAC inhibitor
Remetinostat (SHP-141) is a hydroxamic acid-based inhibitor of histone deacetylase enzymes (HDAC) which is under development for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. -
PAD inhibitor
Cl-amidine is a peptidylarginine deminase (PAD) inhibitor, with an IC50 5.9 μM for PAD4. -
HDAC inhibitor
Resminostat, also known as RAS2410, is a potent inhibitor of histone deacetylase (HDAC) classes I and II. It binds to and inhibits HDACs leading to an accumulation of highly acetylated histones. -
pan-JAK inhibitor
PF-06263276 (PF 6263276) is a potent and selective pan-JAK inhibitor, with IC50s of 2.2 nM, 23.1 nM, 59.9 nM and 29.7 nM for JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK2, respectively. -
HDAC4 inhibitor
Tasquinimod is an orally active antiangiogenic agent by allosterically inhibiting HDAC4 signalling. -
HDAC6 inhibitor
ACY-241 is a new, selective and orally available inhibitor of HDAC6.- Bae J, .et al. , Leukemia, 2018, Sep;32(9):1932-1947 PMID: 29487385
-
Menin-MLL interaction inhibitor
MI-2 (Menin-MLL inhibitor 2) specifically binds to Menin and inhibits Menin??s interaction with MLL fusion proteins in cells. It can effectively reverse MLL fusion protein?Cmediated leukemic transformation by downregulating the expression of target genes downstream of MLL fusion protein oncogenic activity. MI-2 is a new tool for better understanding MLL-mediated leukemogenesis and represents a new approach for studying the role of Menin as an oncogenic cofactor of MLL fusion proteins. -
PAD4 inhibitor
GSK484 hydrochloride (GTPL8577) is a selective and reversible peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PAD4) inhibitor. -
Lin28-let-7a antagonist
Lin28-let-7a antagonist 1 shows a clear antagonistic effect against the Lin28-let-7a interaction with an IC50 of 4.03 μM for Lin28A-let-7a-1 interaction. -
JAK1 inhibitor
GLPG0634 is an orally-available, selective inhibitor of JAK1 (Janus kinase 1) being developed by Galapagos for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and potentially other inflammatory diseases.- Keisuke Nishimura, .et al. , Arthritis Rheumatol., 2015, Apr;67(4):893-902 PMID: 25545152
-
SMYD2 inhibitor
AZ505 ditrifluoroacetate is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the oncogenic protein SMYD2(IC50=0.12 uM) with potential anticancer activity, >600 fold than SMYD3(IC50>83.3 uM); DOT1L(IC50>83.3 uM);EZH2(IC50>83.3 uM). -
JAK2/HDAC dual inhibitor
JAK/HDAC-IN-1 is a potent JAK2/HDAC dual inhibitor, exhibits antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities in several hematological cell lines. -
CDK/JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor
SB1317 is a potent inhibitor of Cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) with IC50 values of 13nM, 56nM and 73nM for CDK2, JAK2 and FLT3, respectively. -
JAK inhibitor
JAK Inhibitor I is a potent, reversible, cell-permeable, and ATP-competitive inhibitor of JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3. -
Aurora kinase A inhibitor
TC-A-2317 hydrochloride is a potent Aurora kinase A inhibitor (Ki = 1.2 nM compared to 101 nM for inhibition of Aurora kinase B). Selective over 60 other kinases (IC50 values > 1000 nM). Exhibits good cell permeability and antitumor activity. -
EZH2 inhibitor
3-deazaneplanocin A, also known as DZNep, is a well-known histone methyltransferase inhibitor, which disrupts polycomb-repressive complex 2 (PRC2), and induces apoptosis, while inhibiting proliferation and metastasis, in cancer cells, including acute myeloid leukemia, breast cancer and glioblastoma.